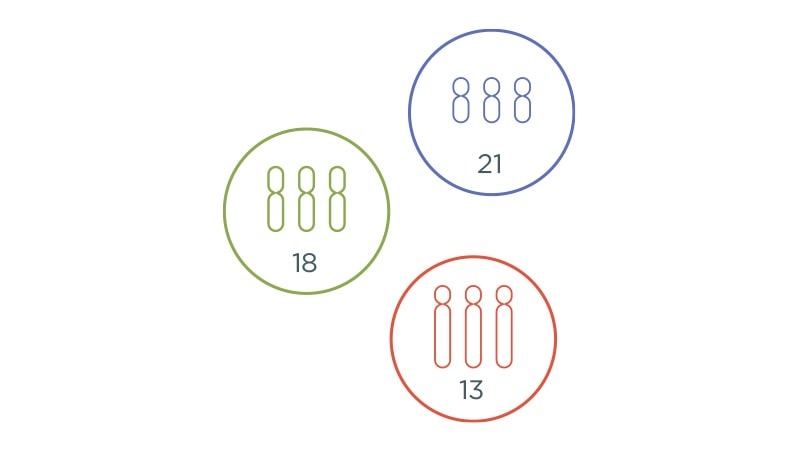
Trisomies
Our cells usually have 23 pairs of chromosomes. Trisomy is the word used to describe the presence of an extra chromosome in the cells. Trisomies are named based on which chromosome has the extra copy, so a person with trisomy 21 has an extra copy of chromosome 21. The Harmony test looks for trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), trisomy 18 and trisomy 13.
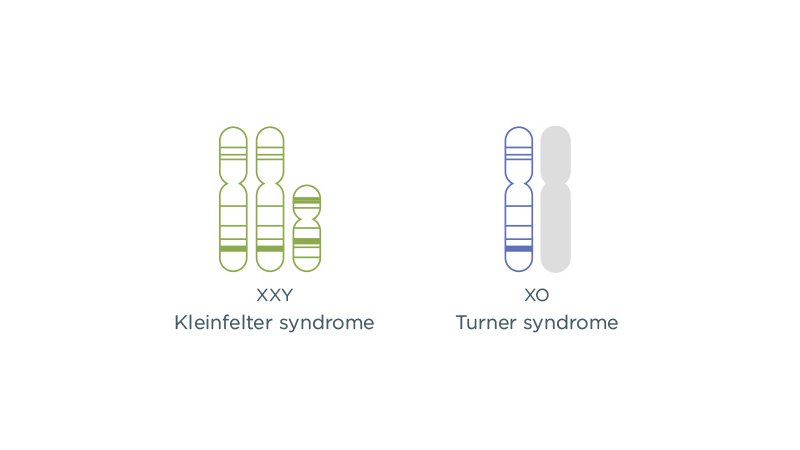
Sex Chromosome Aneuploidies (SCA)
Most people have either two X chromosomes or one X and one Y chromosome in their cells. People with a sex chromosome aneuploidy (SCA) have a different number of X and/or Y chromosomes. The Harmony test looks for SCAs such as:
● XXY (a cause of Klinefelter syndrome)
● Monosomy X (a cause of Turner syndrome)
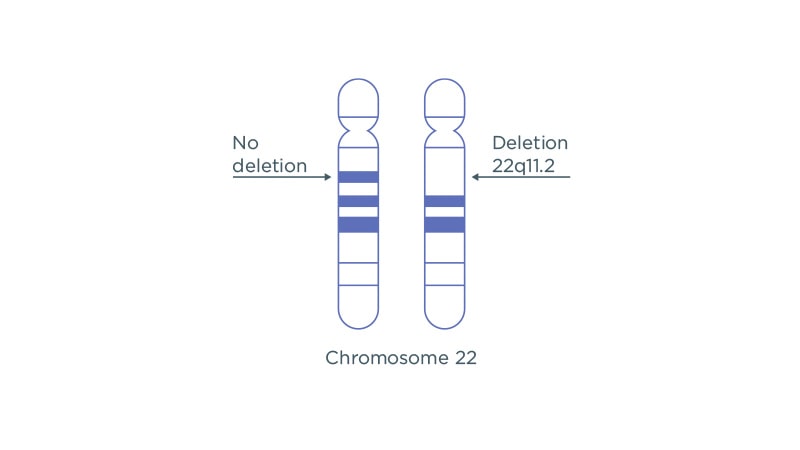
22q11.2 Microdeletion
A microdeletion is the absence of a small piece of chromosome and is named by the area of the chromosome that is absent. The Harmony test looks for 22q11.2 microdeletion, the most common genetic cause of intellectual disability and heart defects after Down syndrome.1,2
References
- Rauch et al. Am J Med Genet A 2006;140:2063-2074.
- Schmid et al. Fetal Diagn Ther 2017; doi: 10.1159/000484317.
